Rethinking Racing Weight: Navigating Performance and Nutrition Beyond the Scale
Jan 29, 2024
Racing weight is a term a lot of endurance athletes are familiar with. It is based on the premise that racing at a lower body weight will improve sports performance and achieve faster times.
Because of this principle, many endurance athletes frequently find themselves restricting their food intake in the hopes of getting leaner to achieve peak performance.
Thankfully, current sports nutrition evidence demonstrates that food’s true benefit lies in what we need to add and not so much in what needs to be subtracted.
These are the main reasons why achieving a racing weight shouldn’t be your top priority:
1. There is no evidence of a real benefit
This one shocked me. For years we’ve been told that leaner and lighter athletes achieve better results than their heavier counterparts. However, no data demonstrate that getting an athlete to drop weight and fat ahead of the competition is beneficial. In other words, Joe at 60kg may perform better than Peter at 65 kilograms, but nothing is demonstrating that asking Peter to aim for a racing weight 5kg lighter will improve his sports performance.
There is, however, plenty of evidence demonstrating the harmful impact energy restriction has on performance and health.
2. Losing weight requires a caloric deficit
This is achieved by either reducing energy intake, increasing energy expenditure or both. However, restricting energy intake can put the athlete at risk of developing energy deficiency, ultimately significantly compromising their performance.
3. Underminishes other nutrition benefits
Someone concerned with looking after their weight is less likely to do carb-loading, include nutrition during long training sessions and prioritise recovery after training. As a consequence, they are missing meaningful opportunities for supporting training adaptations and getting the most out of training.
4. Leads to frustration
Often, racing weight goals don't consider the athlete’s body composition, body weight fluctuations, and overall individual circumstances, making these goals very unrealistic.
Additionally, restricting calories does not always translate into weight loss. Your body’s priority is survival. When energy is missing, it conducts adaptations to preserve energy. Therefore, you are constantly tired and cranky, craving high-calorie foods and struggling to perform at the expected level.
5. Poses a health risk
Relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) is a severe problem. Consequences include impairments of metabolic rate, menstrual function, bone health, immunity, protein synthesis and cardiovascular health. In addition, weight-loss attempts and the desire to be leaner are risk factors for RED-S.
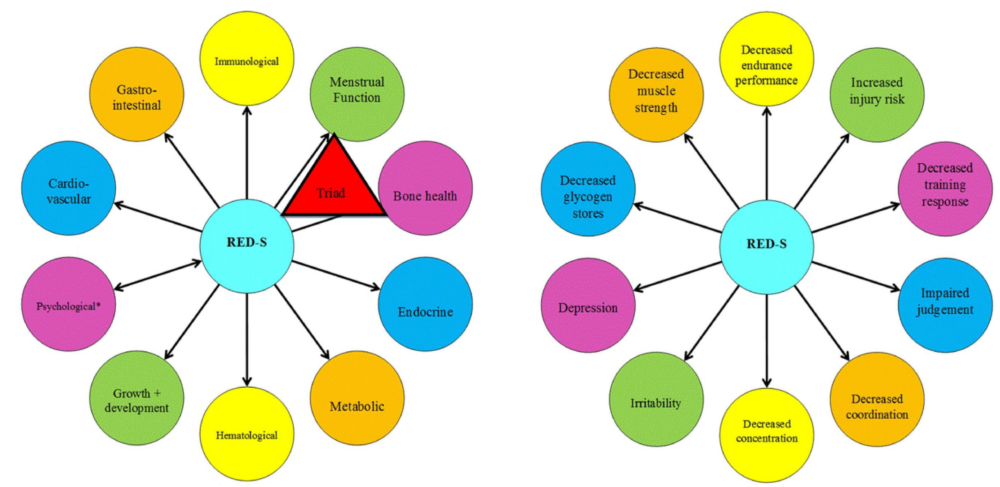
Health (left) and performance (right) consequences of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) Source: IOC consensus statement on relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S): 2018 update
What can you do instead?
I’m not saying that weight loss can’t happen. What I’m saying is that it needs to stop being your focus. Fuelling your body right, getting quality training sessions and prioritising your body’s overall recovery and ability to support the training adaptations will bring you better results than keeping a close eye on the scale.
I love the way Jesse Thomas talks about this after overcoming an eating disorder that put his career and life at risk. “Don’t aim for a number on the scale. Aim for consistently healthy habits (...) If you eat consistently healthy, sleep well, and get your workouts in, your body will adjust to the appropriate weight, and that is your ideal race weight.”
References:
- Mountjoy, M., Sundgot-Borgen, J., Burke, L., Ackerman, K. E., Blauwet, C., Constantini, N., ... & Budgett, R. (2018). International Olympic Committee (IOC) consensus statement on relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S): 2018 update. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 28(4), 316-331.
- Tomiyama, A. J., Ahlstrom, B., & Mann, T. (2013). Long‐term effects of dieting: Is weight loss related to health?. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 7(12), 861-877.
- Hicks, L. (2020, July 29). For young female athletes, losing weight may not improve performance. Retrieved from https://www.science.org/content/article/young-female-athletes-losing-weight-may-not-improve-performance
- Tornberg, Å. B., Melin, A., Koivula, F. M., Johansson, A., Skouby, S., Faber, J., & Sjödin, A. (2017). Reduced neuromuscular performance in amenorrheic elite endurance athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 49(12), 2478-2485.
Join the Fuelling with Purpose Newsletter!
Subscribe to my weekly newsletter and receive endurance nutrition tips, product recommendations, and energy-packed recipes delivered straight to your inbox.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at anytime.

